POST请求主要包含json格式、xml格式、文件上传(form-data)、及默认传递的urlencoded。
HTTP的报文结构:
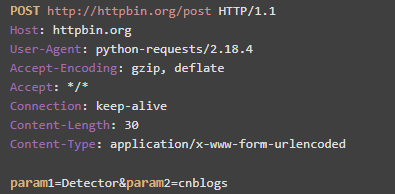
1.请求行:请求方法、请求URL、HTTP协议版本三个部分
2.请求头:从第二行开始到倒数第二行都是我们的请求头(headers)
3.消息主体:截图的最后一样是请求体,也就是我们要发送数据的主体,消息主体
也就是说一个正常的post请求主要由请求行,请求头,消息主体组成。
我们要知道post请求四种传送正文方式首先我们要先了解一下常见的四种编码方式:
HTTP协议规定POST提交的数据必须放在消息主体中,但协议并没有规定数据必须使用什么编码格式。常见的四种编码方式如下:
1.application/x-www-form-urlencoded
这是最常见的POST提交数据的方式了。浏览器的原生form表单,如果不设置enctype属性,那么最终就会以appliaction/x-www-form-urlencoded方式提交数据。请求类似下边这样。
POST http://www.example.com HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=utf-8 title=test&sub%5B%5D=1&sub%5B%5D=2&sub%5B%5D=3
2.multipart/form-data
除了传统的表单,我们另一个经常用到的上传文件用的表单,这种表单类型为multipart/form-data
这又是一个常见的post数据提交的方式,我们使用表单上传文件时,必须让form的enctyped等于这个值
3.application/json
application/json这个content-type作为响应头大家肯定不陌生。实际上,现在越来越多的人把它当做请求头,
用来告诉服务器消息主体是序列化后的json字符串,由于json规范的流行,除了低版本IE之外的各大浏览器都支持JSON.stringify
服务器语言也都有处理JSON的函数,使用json不会遇上什么麻烦。
4.text/xml
它是一种HTTP作为传输协议,XML作为编码方式的远程调用规范
post请求四种传送正文方式:
(1)请求正文是application/x-www-form=urlencoded
形式:
requests.post(url=”,data={‘key1′:’value1′,’key2′:’value2’},headers={‘Content-Type’:’application/x-www-form-urlencoded’})
requests支持以form表单形式发送post请求,只需要将请求的参数构造成一个字典,然后传给request.post()的data参数即可。
输入:
url = ‘http://httpbin.org/post’ d = {‘key1’: ‘value1’, ‘key2’: ‘value2’} r = requests.post(url, data=d) print r.text
输出:
{ “args”: {}, “data”: “”, “files”: {}, “form”: { “key1”: “value1”, “key2”: “value2” }, “headers”: { …… “Content-Type”: “application/x-www-form-urlencoded”, …… }, “json”: null, …… }
可以看到,请求头中的content-Type字段已设置application/x-www-form-urlencoded,且d = {‘key1’: ‘value1’, ‘key2’: ‘value2’}
以form表单的形式提交到服务器,服务器返回的form字段即是提交的数据
(2)请求正文是multipart/form-data
形式:
requests.post(url=”,data={‘key1′:’value1′,’key2′:’value2’},headers={‘Content-Type’:’multipart/form-data’}) 发送文件的数据需要(安装requests_toolbelt) from requests_toolbelt import MultipartEncoder import requests
m = MultipartEncoder( fields={‘field0’: ‘value’, ‘field1’: ‘value’, ‘field2’: (‘filename’, open(‘file.py’, ‘rb’), ‘text/plain’)} )
r = requests.post(‘http://httpbin.org/post’, data=m, headers={‘Content-Type’: m.content_type})
不需要文件
from requests_toolbelt import MultipartEncoder import requests
m = MultipartEncoder(fields={‘field0’: ‘value’, ‘field1’: ‘value’})
r = requests.post(‘http://httpbin.org/post’, data=m, headers={‘Content-Type’: m.content_type})
(3)请求正文是raw
形式:
♦传入xml格式文本 1 requests.post(url=”,data='<?xml ?>’,headers={‘Content-Type’:’text/xml’}) ♦传入json格式文本 1 requests.post(url=”,data=json.dumps({‘key1′:’value1′,’key2′:’value2’}),headers={‘Content-Type’:’application/json’})
或者:
1 requests.post(url=”,json={{‘key1′:’value1′,’key2′:’value2’}},headers={‘Content-Type’:’application/json’})
♦可以将一json串传给requests.post()的data参数,
输入:
url = ‘http://httpbin.org/post’ s = json.dumps({‘key1’: ‘value1’, ‘key2’: ‘value2’}) r = requests.post(url, data=s) print r.text
输出:
{ “args”: {}, “data”: “{\”key2\”: \”value2\”, \”key1\”: \”value1\”}”, “files”: {}, “form”: {}, “headers”: { …… “Content-Type”: “application/json”, …… }, “json”: { “key1”: “value1”, “key2”: “value2” }, …… }
(4)请求正文是binary
形式:
1 requests.post(url=”,files={‘file’:open(‘test.xls’,’rb’)},headers={‘Content-Type’:’binary’})
♦Requests也支持以multipart形式发送post请求,只需将一文件传给requests.post()的files参数即可。
输入:
url = ‘http://httpbin.org/post’ files = {‘file’: open(‘report.txt’, ‘rb’)} r = requests.post(url, files=files) print r.text
输出:
{ “args”: {}, “data”: “”, “files”: { “file”: “Hello world!” }, “form”: {}, “headers”: {…… “Content-Type”: “multipart/form-data; boundary=467e443f4c3d403c8559e2ebd009bf4a”, …… }, “json”: null, …… }
文本文件repost.txt的内容只有一行:hello word!从请求的相应结果可以看到数据已上传到服务端
神龙|纯净稳定代理IP免费测试>>>>>>>>天启|企业级代理IP免费测试>>>>>>>>IPIPGO|全球住宅代理IP免费测试





